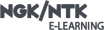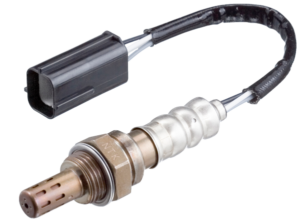
NTK Oxygen Sensors
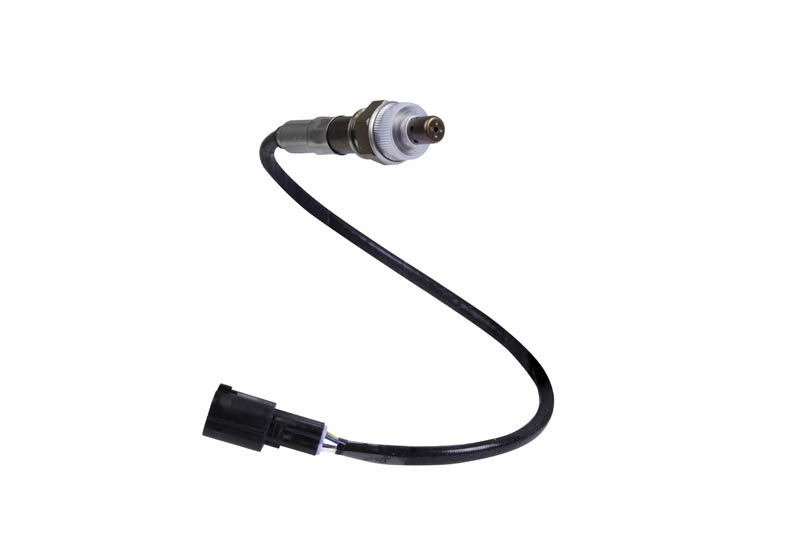
NTK is the world’s largest manufacturer of oxygen sensors. NTK Oxygen Sensors are designed to maintain optimal fuel efficiency and are supplied with a direct-fit connector similar to those used by the OEM manufacturer for easy installation.
Every NTK Oxygen Sensor undergoes a complex three test process, including long life, high temperature & anti poisoning, to guarantee high quality and durability. As future emissions standards become tougher, NTK is further developing oxygen sensor technologies to help provide cleaner, more efficient engines.
What is an Oxygen Sensor?
An oxygen sensor continually detects the oxygen content in the exhaust gases of an engine. The oxygen sensor output signal informs the vehicle’s ECU (Electronic Control Unit) whether the AFR (Air-Fuel Ratio) is lean or rich. Based on this, the ECU adjusts the amount of fuel injected into the engine to achieve an optimal AFR.
NTK Different Oxygen Sensors
NTK manufacture three different types of oxygen sensors:
TITANIA OXYGEN SENSORS
Vary in resistance based on the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
ZIRCONIA OXYGEN SENSORS
Produce a voltage which varies based on the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
Both Zirconia and Titania oxygen sensor types are produced with different numbers of wires to satisfy different needs, although it is critical to note that due to their different properties Zirconia and Titania sensors should not be interchanged under any circumstance.
AIR FUEL RATIO SENSORS
Exhaust gas enters the air/fuel ratio sensors measuring cell through porous diffusion channels. In the cell, the oxygen density is measured by means of electrodes and compared with that of stoichiometric.
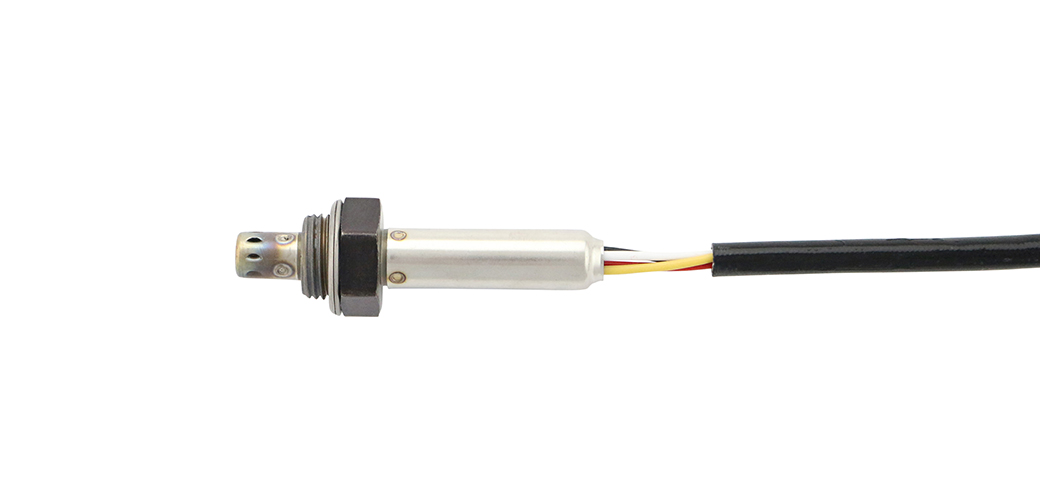
Details
Titania
One wire is the sensor signal, one is the isolated sensor signal ground and the remaining two are used to supply a voltage to the internal heater.
Also referred to as an ISO – HEGO Sensor (Isolated Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor).
The sensor signal wire is directly connected to one of the platinum electrodes on the ceramic element. The sensor output is immune to ground loop voltages and also to large resistances in the vehicle ground return, caused by corroded connections. No NTK four wire sensor is case grounded. Case grounded sensors have the ground wire physically attached to the sensor body.
It is not recommended to replace isolated ground sensors with case ground types.
Details
Zirconia
One wire is the sensor signal, one is the isolated sensor signal ground and the remaining two are used to supply a voltage to the internal heater.
Also referred to as an ISO – HEGO Sensor (Isolated Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor).
The sensor signal wire is directly connected to one of the platinum electrodes on the ceramic element. The sensor output is immune to ground loop voltages and also to large resistances in the vehicle ground return, caused by corroded connections. No NTK four wire sensor is case grounded. Case grounded sensors have the ground wire physically attached to the sensor body.
It is not recommended to replace isolated ground sensors with case ground types.
Details
Air Fuel Ratio
For Air Fuel Ratio Sensors the wiring configuration is as below:
- The yellow wire is for the heater ground via ECU/ECM
- The blue wire is the heater’s positive feed
- The white wire is for the pump current (Ip)+
- The grey wire is for measuring the chamber voltage (Vs)+
- The black wire is for the pump current (Ip)-
Part Numbering System
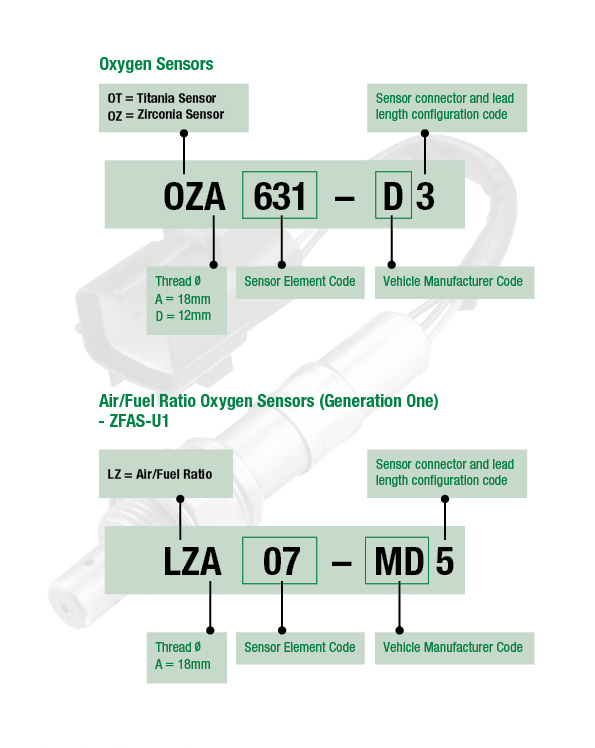
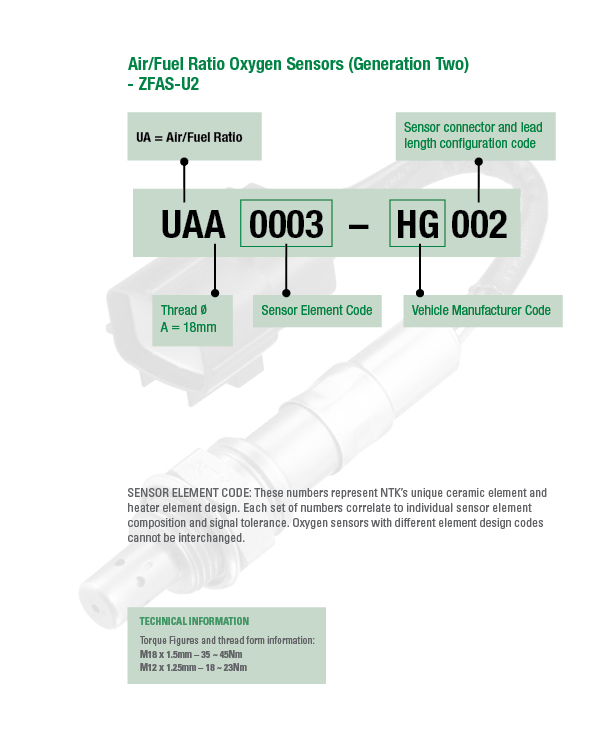
SENSOR ELEMENT CODE: These numbers represent NTK’s unique ceramic element and heater element design. Each set of numbers correlate to individual sensor element composition and signal tolerance. Oxygen sensors with different element design codes cannot be interchanged.